A greenhouse is a system for modifying and managing environmental factors that allows plants to grow in a suitable and controlled climate during different seasons of a year. Greenhouse technology becomes important in climate change, which emphasizes high-quality production with higher productivity from available resources. However, the productivity and efficiency of greenhouse technology is completely dependent on the types of greenhouse structures used for production. Recent trends in human population growth, along with advancing consumption patterns, emphasize the development of innovative greenhouse structures.
The type and equipment of the greenhouse structure used in each region generally corresponds to the local environment, the availability of building materials and the specific product. In each region, components such as cover materials, climate control systems, irrigation and fertilization equipment are regularly evaluated by farmers, designers and researchers to improve their efficiency, reduce inputs and reduce adverse environmental impacts.
The efficiency and productivity of greenhouse operations largely depends on the type of structure used. Since there are many greenhouse designs to choose from for a specific area, it is very important to know the pros and cons of each type and structure of the greenhouse. Therefore, we will briefly discuss the types of greenhouse structures and their components.
Types of greenhouses in terms of structure (separate or connected):
• Single unit greenhouses
• Multi-unit greenhouses (next to each other)

Classification of the greenhouse in terms of temperature:
- Cold greenhouse
- Semi-warm greenhouse
- Warm greenhouse
- Warm and humid greenhouse
In general, the greenhouse structure in Iran is based on two arch and peak designs. According to the environmental conditions of each region, greenhouse structures have different shapes in terms of slope and size. In general, the greenhouse is used to achieve important goals, including maximum light reception and maximum productivity from less land area.
Types of tunnel greenhouses:
- Single unit
- Multiple units (composite)
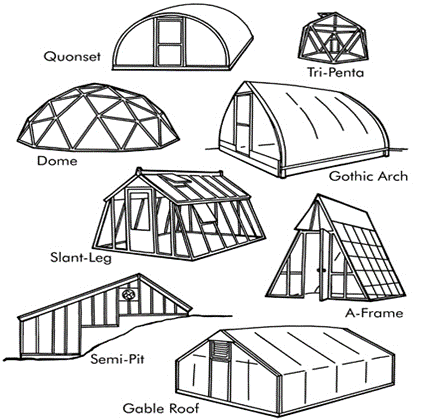
In reviewing the types of greenhouses, we refer to 4 general forms:
Tunnel greenhouses (Quonset)
One of the most common greenhouses in the world are tunnel greenhouses, which are very easy and affordable to build. Tunnel greenhouses are also known as Quast or cylindrical greenhouses. Types of tunnel greenhouse structures are relatively cheap and quickly installed, and due to their curved shape, they have high resistance to wind and snow. It also allows plants to receive maximum sunlight. Tunnel greenhouses are the most profitable compared to other greenhouses by increasing the growth period of plants. If the tunnel is made high, the plants will grow in a more controlled climate, minimizing the effect of hot or cold weather.

Characteristics of tunnel greenhouses
Construction of tunnel greenhouse has different designs depending on the type of product produced, climatic conditions and land area, in general, the length of tunnel greenhouses varies depending on the land area and their width is approximately 6 to 12 and 2 to 4 in height.
• They have an arched roof (they do not have the durability of Spanish greenhouses).
• Smaller dimensions than other greenhouses (reducing the need for energy for heating and air conditioning)
• Lower construction cost
• High resistance of the structure (made of galvanized steel)
Advantages of tunnel greenhouse:
• Higher yield compared to continuous greenhouses.
• Resistant to wind flow.
• 40% reduction in fossil energy consumption (for double-clad structures).
• Increasing the level of plant protection (reducing the use of poisons and chemicals).
• Cheap and affordable (compared to other greenhouses).
• Ability to install temporarily.
• Reduce costs and save time.
Circular greenhouses
Greenhouses with a circular structure have a full arched roof. These greenhouses catch the sun all day long because their structure is usually north-south. Normally, there is no scaffolding in circular greenhouses, and summer crops are grown on the floor of the greenhouse. The cover of circular greenhouses is usually made of plastic.
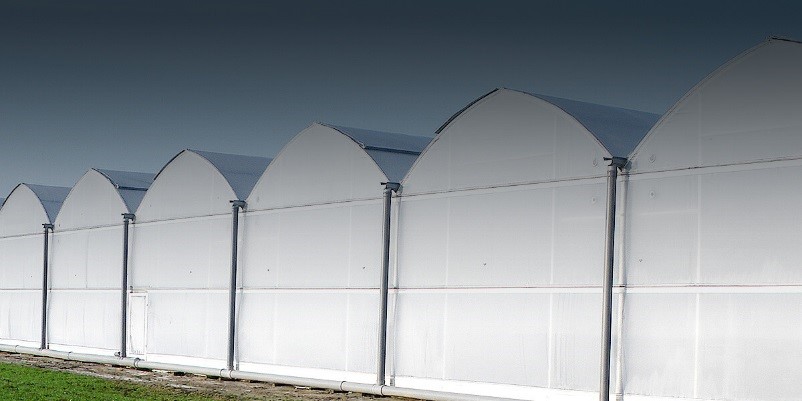

Advantages of circular greenhouses:
• More stability during wind blowing (lowest aerodynamic resistance to wind)
• Affordable
• Direct sunlight throughout the day
• Maximum ventilation in the greenhouse (minimum coverage level)
Gable roof greenhouses
The cost of building a greenhouse in all types of Gable roof greenhouse structures is higher than other greenhouses. Gable roof greenhouses have roofs with a slope of 25 to 30 degrees, vertical walls and the most resistant greenhouse structure against snow. The ability to transmit high light in this type of greenhouse, which is mostly used in cold regions, is one of the most important advantages of Gable greenhouses. The cost of building all kinds of glass greenhouses is a bit high, and this makes other structures to replace them.

Gothic arch greenhouses
The design of Gothic greenhouse structures is a combination of peak and circular greenhouse structures. The shape of the roof in Gothic greenhouses is in the form of an angular bow. Gothic structure type is one of the strongest greenhouse and its appearance is similar to traditional greenhouses.
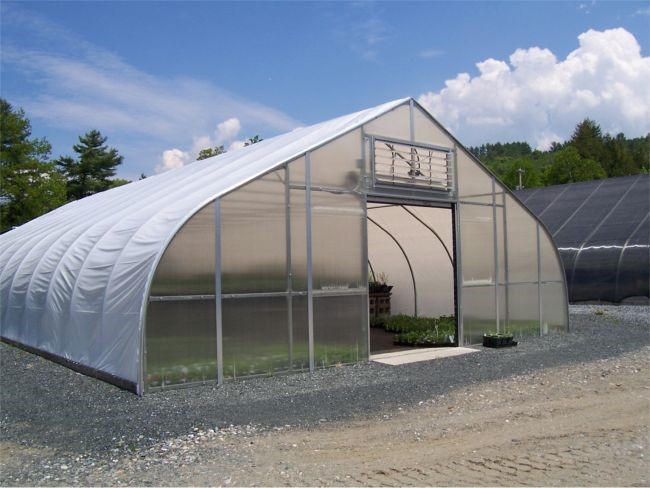

The advantage of building all kinds of Gothic greenhouses:
• Relatively high resistance to strong wind and heavy snowfall
• Special design for the roof (so that a drop of water does not drip on the plant)
Conclusion:
The division of greenhouses has been discussed and investigated by many greenhouse owners and farmers from different aspects, and we will continue this discussion in the next articles to explain other types of greenhouse constructions.
• Fatemeh safaei / 00989103218554
• Faegheh osanlou/ 00989904823436
• WWW.TIDAPARS.COM
• IG: TIDAPARS








